Python is not recognized as an internal or external command

ADVERTISEMENT
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Overview
- Specify the full location to python.exe
- Add the full location of python.exe to PATH
- Manually
- Summary
- Next Steps
Introduction
One of the most frustrating aspects of learning how to code in Python doesn't even involve any coding itself. For many beginners, simply getting Python to run on their local machine can present a significant challenge.
Windows users in particular may find themselves greeted with a strange and convoluted error message when trying to run Python from the Command Prompt: 'python' is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file.
In this article, you'll take a closer look at the error 'python' is not recognized as an internal or external command and see a few quick fixes for it.
Note that the exact spelling of this error could vary slightly, and this article may help you if you're encountering similar errors that include messaging like Python Not Found or Python Was Not Found.
Overview
You may have seen this error if you're running Python on a Windows machine. If you're a Linux or Mac user, then skip to the section titled, "What if I'm on a different operating system?". But before we discuss how to fix this error, let's get a better understanding of why it occurs.
Once Python is installed on your Windows machine, you'll likely try to run it in one of two ways.
The first way is to locate the Python executable on your system and double-click on it. This is the actual executable file for Python itself, which you downloaded from the official Python downloads page.
This will open up the Python IDE in a separate window, and you'll be able to code in the interactive interpreter:
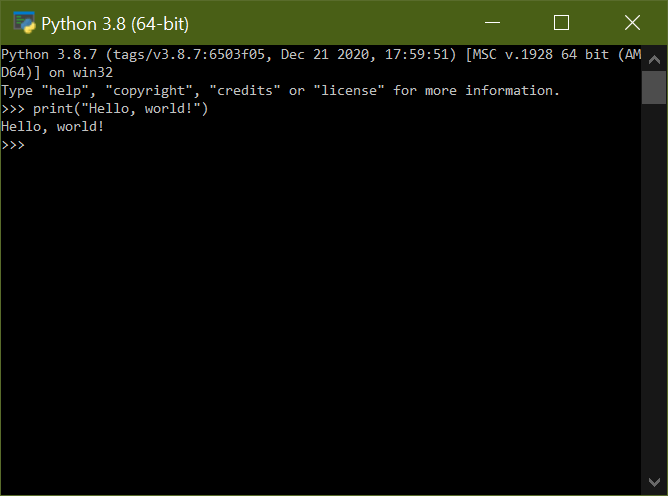
The second way is to open up a Command Prompt, type the word python, and press Enter. Ideally, this would open up an instance of Python in the same window:
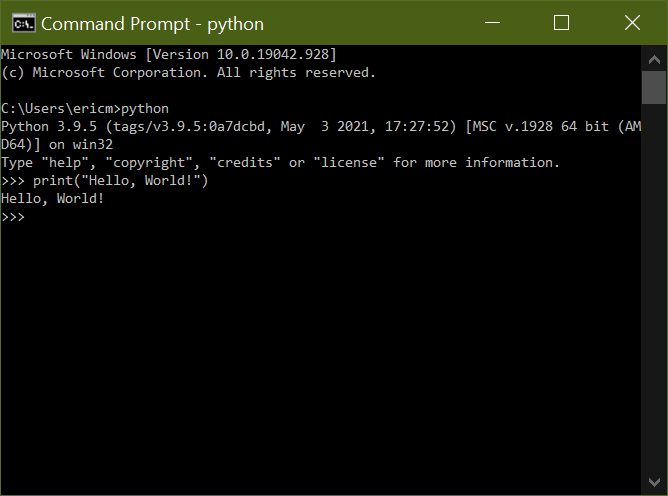
Unfortunately, there's also a chance that you could come up against this error:
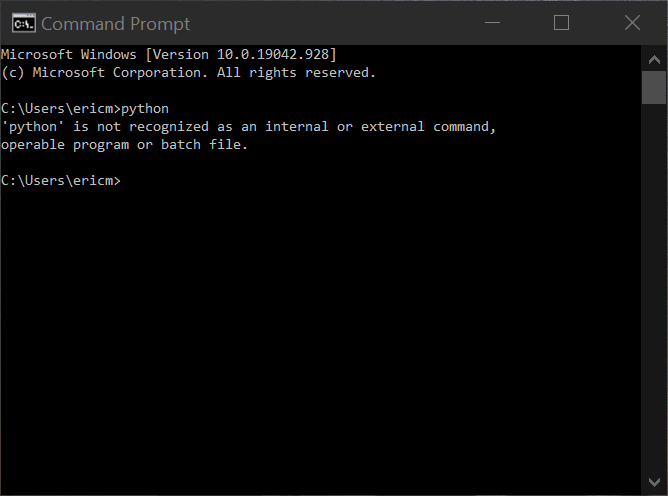
In this case, you'll be greeted instead with an error message that reads, "'python' is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file."
So, what does this strange error mean, and why are you seeing it? Well, whenever you run a program on your machine, your computer needs to know exactly where on your machine that program file is located so it can be executed.
When you navigated to the folder that contained the executable Python file and clicked on it, Windows knew exactly what file you wanted it to run, and opened the Python interpreter with no problems.
However, when you try to run a program from the Command Prompt, Windows will only run that program if it already knows where on your machine that file is located. It does this via the PATH environment variable.
Environment variables tell the computer facts about the runtime environment of the current operating system. For example, USER will tell the computer system who the current logged-in user is, and HOME will give the location of that user's home directory.
The PATH environment variable tells the system which directories it should look in for executable programs. When a user types a program name in the Command Prompt and doesn't specify the exact file location of that program, then the computer system will search all of the directories listed in the PATH to find the location of the file and execute it.
This means that if the directory that holds the program you want to execute is not listed in the PATH environment variable, then Windows won't search that folder for any executable files. In other words, it will never find Python and won't be able to execute it from the Command Prompt.
In the next couple of sections we will discuss how to fix: 'python' is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file
There are several ways to fix this error, but let's take a look at some of the most common.
Specify the full location to python.exe
You learned previously that this error occurs when Windows can't find the location of the Python executable file.
One way to fix the error would be to launch Python from the Command Prompt by passing in the full path to the executable file each time you wanted to run Python. In other words, instead of typing Python you would type something like C:\Users\me\path\to\python.exe.
To find the full path, open up the Start menu and search for "Python":
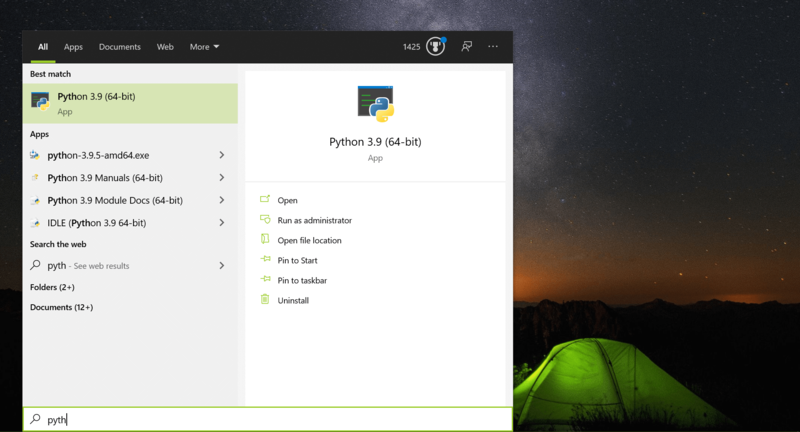
Select Open file location, which should bring up an Explorer window with the folder containing the Python executable. (Note that this may be a shortcut, in which case you'd need to right-click on the Python executable and select Open file location a second time.) In the end, you should see a file called python.exe.
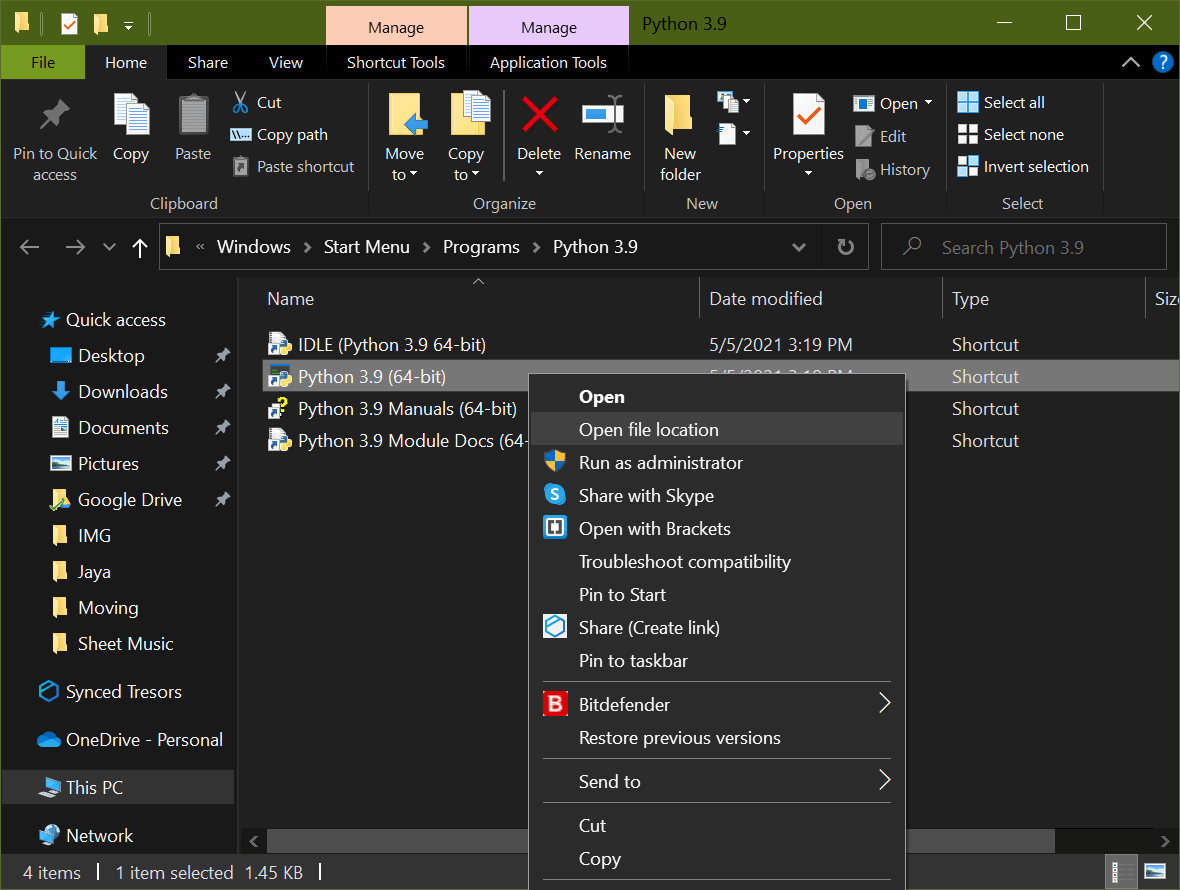
You want to right-click on this file and select Properties:
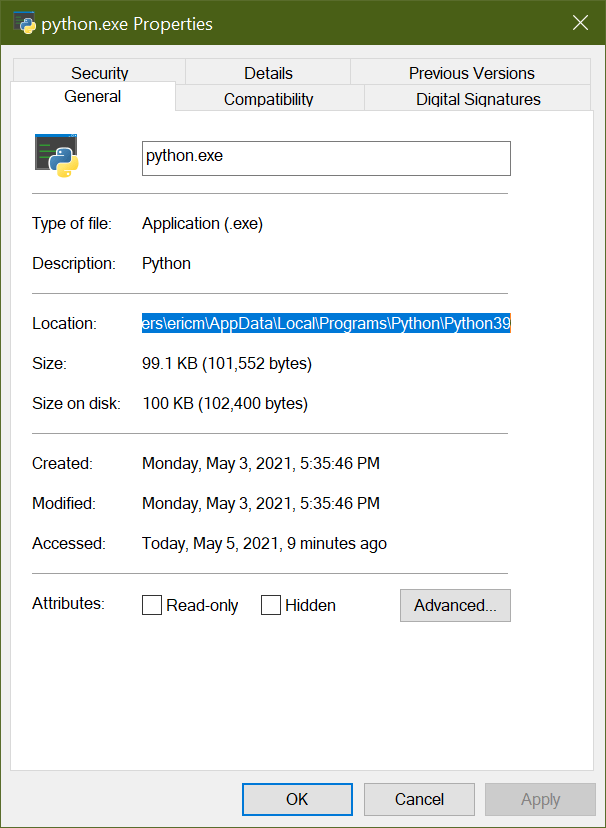
Under the General tab, you'll see an entry titled Location which contains the full system path to this executable file:
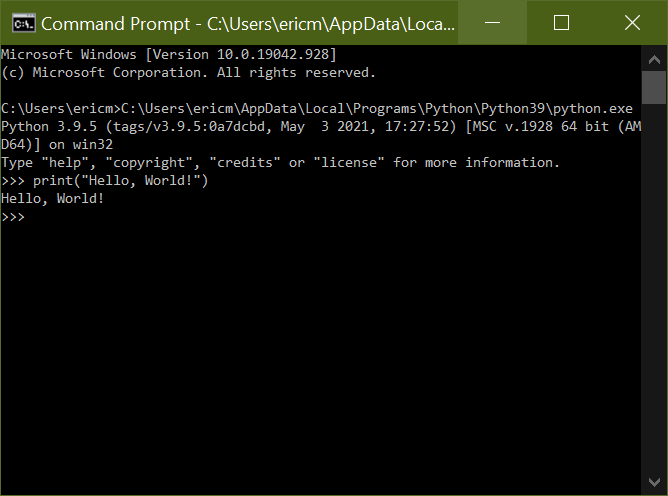
Copy this path and return to the Command Prompt. Paste it in, add a trailing slash and python.exe to denote the program file, and press Enter. Python should launch without issue:
This will successfully allow you to run Python from the Command Prompt. However, the process of locating the exact file path can be tedious, and with this fix, you'd need to provide this every single time you wanted to run Python.
Thankfully, instead of specifying the full path each time, you can simply add this file location to your system PATH.
Add the full location of python.exe to PATH
Recall that the PATH environment variable tells your system which directories it should look in to locate executable programs. In order to be able to run Python from the Command Prompt, you need to make sure that the directory the Python executable file is contained in is listed in the system PATH.
When you first install Python, there is an option you can select to have the installer do this for you:
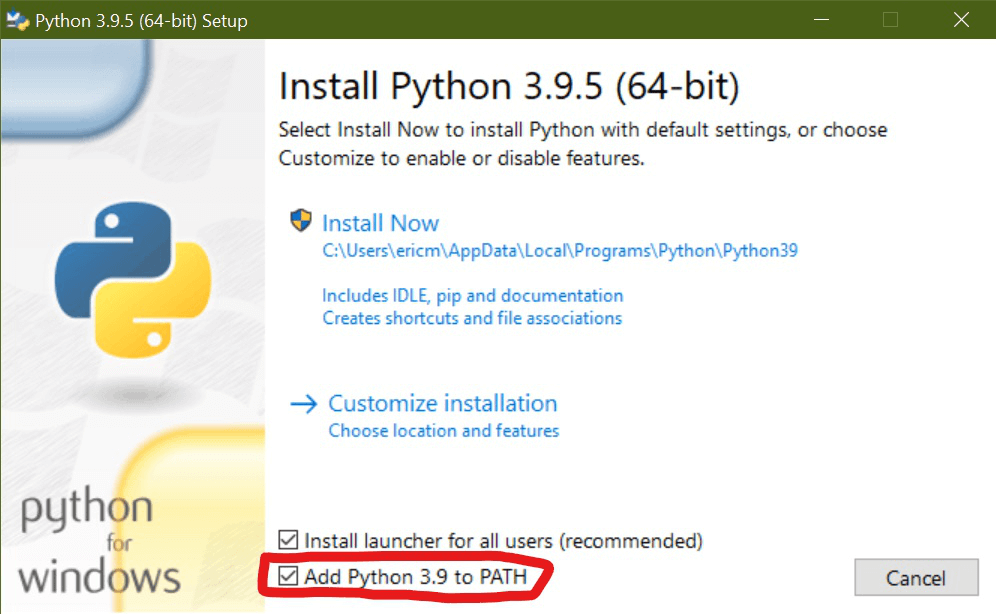
However, if you did not select this option during installation, you can still go back and add it later.
There are two main ways to accomplish this: through the installer and manually.
Installer
When you first download Python from the official Python downloads page, your computer will save an installation file titled python-3.9.5-amd64.exe or something similar to a specified directory, usually your Downloads folder. You can use this same installer to update your Python installation and add its location to your system PATH.
Search for the installer from the Start menu or locate it in your Downloads folder (or whichever folder you downloaded it to). When you click on it this time, instead of asking you to install Python, it should present you with several options for modifying your setup:
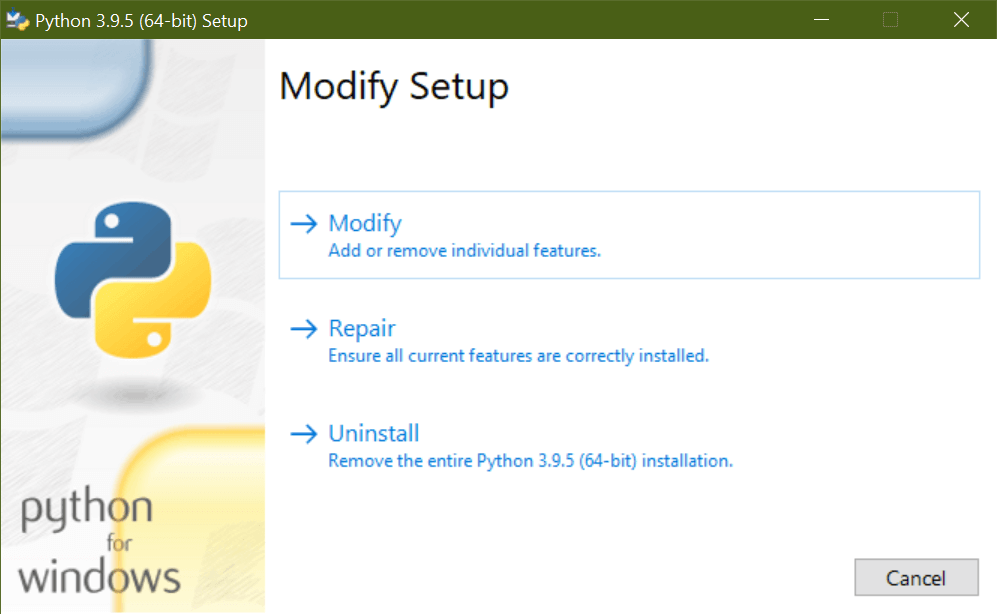
Clicking Modify will take you to the Optional Features page:
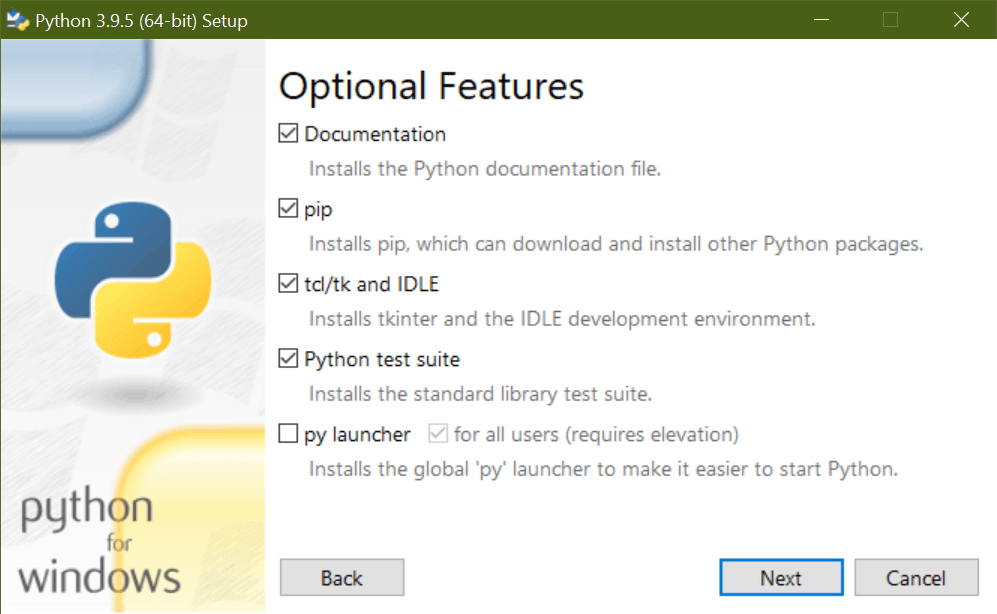
From here, you should click Next until you see the Advanced Options page. On this page, select the checkbox that says Add Python to environment variables:
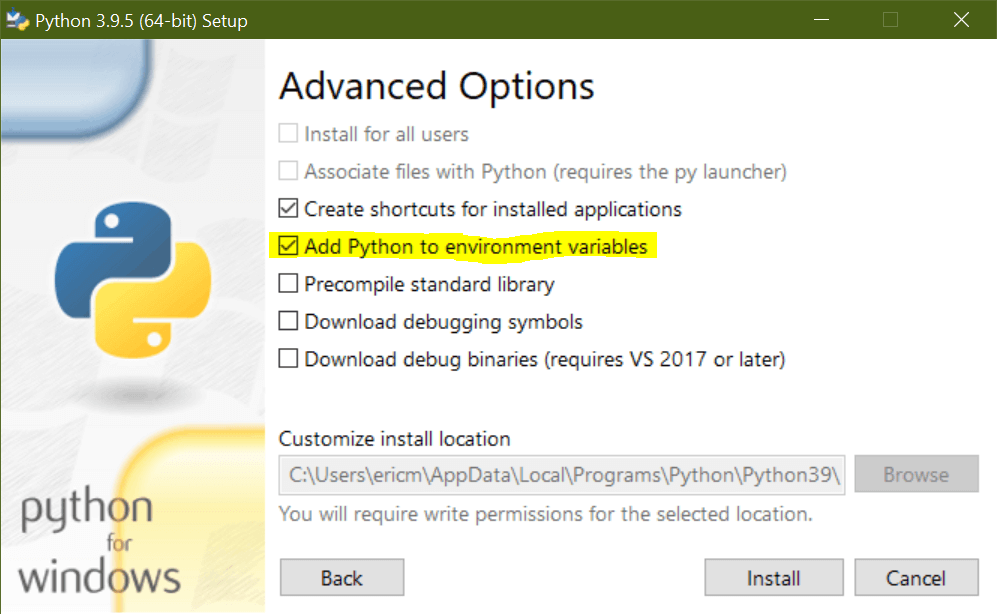
The installer will modify your Python installation and add the executable program location to your system PATH variable. Once the modification is complete, you can open up the Command Prompt and type python to enter the interpreter:

You should see no errors at this point.
Manually
If you can't find where you downloaded the Python installer, or you removed it from your computer already, you can always modify the PATH environment variable yourself. This section walks you through how to accomplish this.
First, you need to have the full path to the directory containing the python.exe program file. (Refer to the section "Specify the full location to python.exe" for how to do this.)
Once you have the file location, you'll need to append it to the end of your system PATH. To modify the path, first open your system settings. You can usually get to the system settings by opening the Start menu and searching for About your PC. Click on Advanced system settings (located in the menu on the right-hand side):
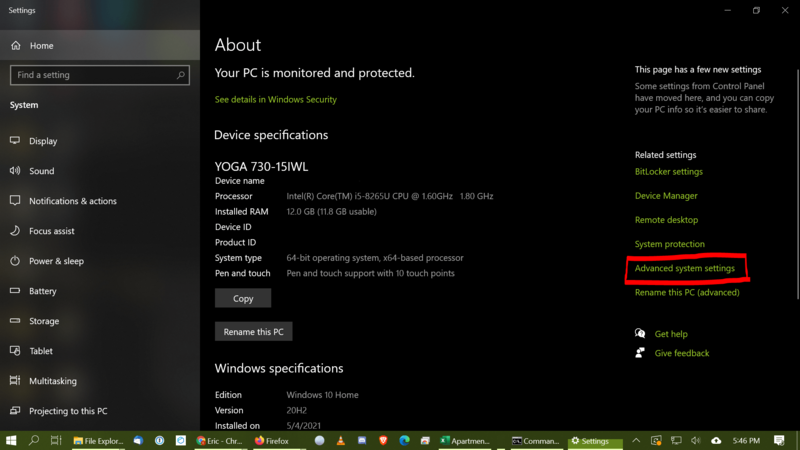
You'll be redirected to a System Properties dialog box. Under the Advanced tab, click Environment Variables:
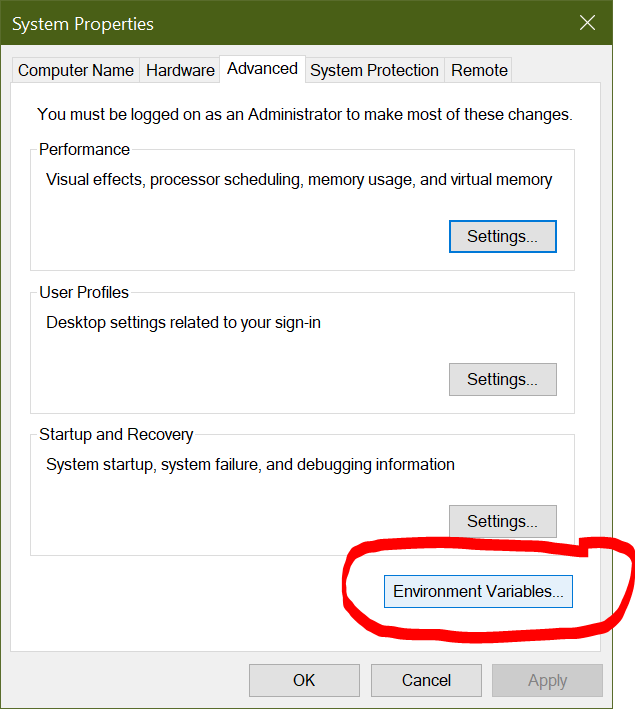
This will open up the Environment Variables dialog box. Here is where your system PATH is defined. This is the variable you'll want to change to tell your Windows machine where to find the Python executable program. Make sure you've selected the path environment variable, then click Edit:
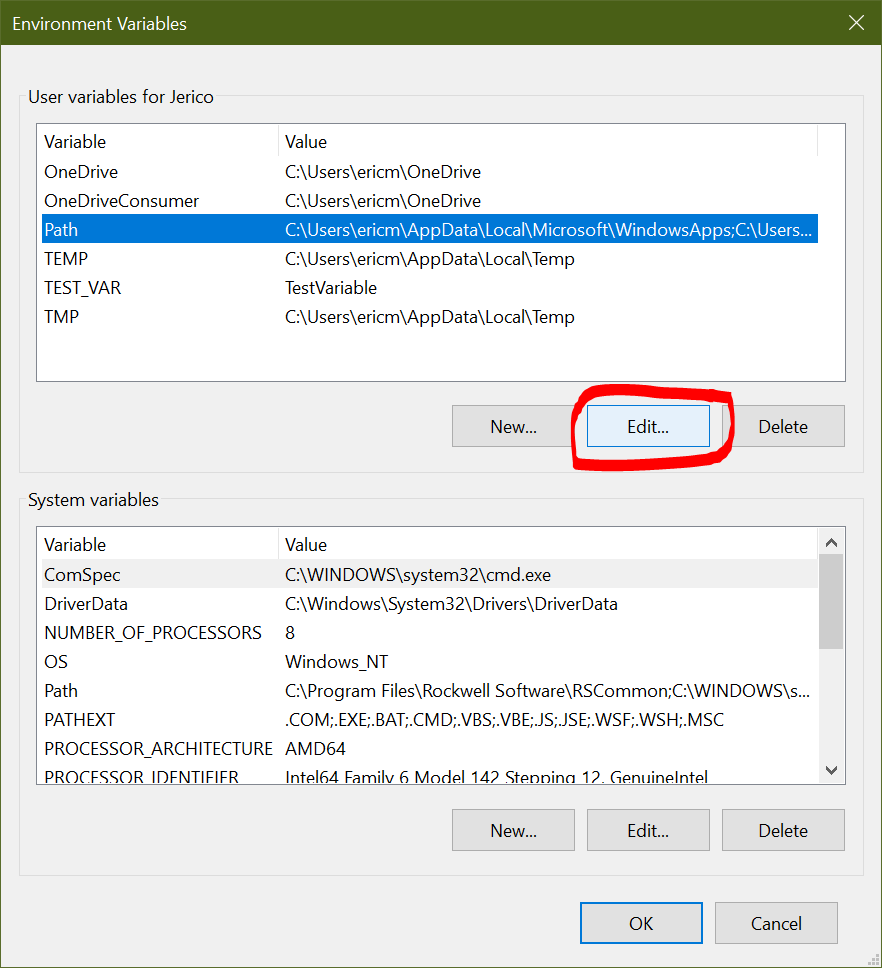
Now, you'll have the option to edit the PATH environment variable. Click New, which should append a new element to the list:
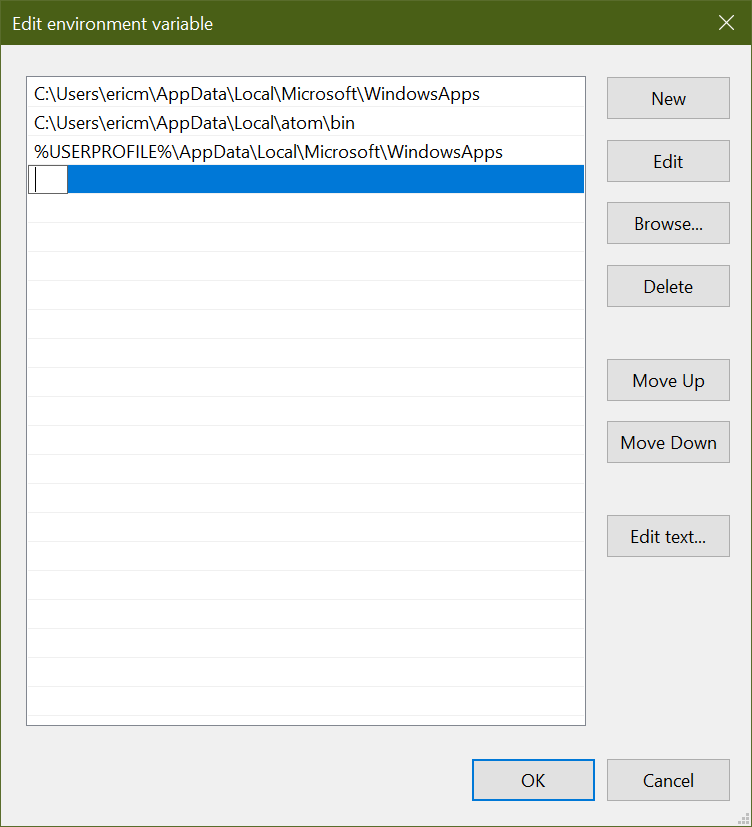
This is where you'll want to enter the full path to the directory containing the python.exe file you located earlier:
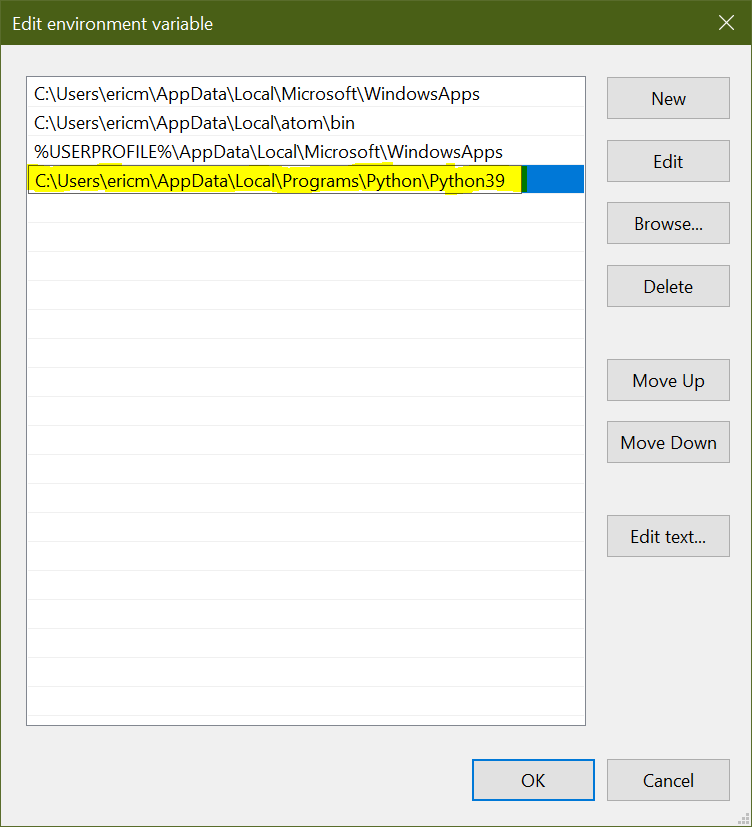
Click OK on each dialog box until you've exited out of all of them completely.
That's it! You should be able to open up a Command Prompt and type python, and the command should execute with no errors:

What if I'm on a different operating system?
The error "'python' is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file" is specific to the Windows operating system. If you're on a different operating system, you likely won't see these exact words. In particular, Unix-based systems like Linux or macOS will say something a little bit different:
user@host:~$ python
bash: python: command not found
In this case, the problem is often the same - the operating system cannot find the python command, because the location of the binary file is not defined in the system PATH.
Luckily, for Unix-based systems, the fix is often much simpler - just check to make sure that you actually have Python installed! These operating systems will typically install Python under /usr/bin or /usr/local/bin, directories which are included in the system path by default.
You can confirm this by echoing the PATH environment variable to stdout:
user@host:~$ echo $PATH
/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:
If you're seeing a python: command not found error on a Unix-like operating system, simply use your package manager to install the latest version of Python and then try running the command again.
Summary
In this tutorial, you saw how to solve an error that many Windows users encounter when they first try to run Python on their machines: 'python' is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file. This error appears on Windows operating systems when the location of the Python executable file has not been properly specified in the system PATH environment variable.
You saw how to circumvent this error by simply specifying the full location to the python.exe file each time you wanted to run Python from the Command Prompt. You also learned how to add this file location to your system PATH so Windows will be able to find it automatically. You did this using the Python installer as well as manually by editing the PATH environment variable.
Finally, you saw a similar error that users of Unix-based systems might come up against, as well as a quick way to solve it.
Next Steps
Congrats! Now that you've got Python up and running on your machine, it's time to dive deep into coding. Looking for the basics to get started? Check out our tutorial on comparing Python strings or using the sum function in Python.
Do be aware that the error you solved in this tutorial won't be the only one you encounter on your Python journey. For example, the return outside function error in Python is another one that's likely to come up early on.
If you're interested in learning more about the basics of Python, coding, and software development, check out our Coding Essentials Guidebook for Developers, where we cover the essential languages, concepts, and tools that you'll need to become a professional developer.
Thanks and happy coding! We hope you enjoyed this article. If you have any questions or comments, feel free to reach out to jacob@initialcommit.io.
Final Notes
Recommended product: Coding Essentials Guidebook for Developers